

- OVERCLOCKING USING INTEL EXTREME TUNING UTILITY HOW TO
- OVERCLOCKING USING INTEL EXTREME TUNING UTILITY MANUAL
You will also need a motherboard that allows for overclocking. To learn more about Intel® processor names and designations, check out this breakdown of CPU names. The K-series and X-series suffix designates that the frequency multipliers on the unit aren’t locked and thus allow for overclocking. You will also need a CPU with a K or X at the end of the name, such as the Intel® Core™ i9-9900K processor. A capable CPU cooler is critical when attempting to overclock. Higher speeds and voltages mean more heat generated by the CPU, and that means a more efficient cooling solution is required for the CPU to safely operate. It’s important that you use an adequate cooling solution when attempting to overclock your CPU. Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s explore the necessary hardware you’ll need in order to attempt an overclock. In addition to adjusting frequencies, the overclocking process might require that you raise select voltages, and adjust other performance settings on the system to maintain stability at high frequencies. We will then continue that process until we reach the limits of what is possible with the hardware. In order to increase the CPU frequency during an overclock, we will be raising the multipliers in +1 intervals, systematically adding 100 MHz to our processor’s frequency at a time, then testing for success and stability.
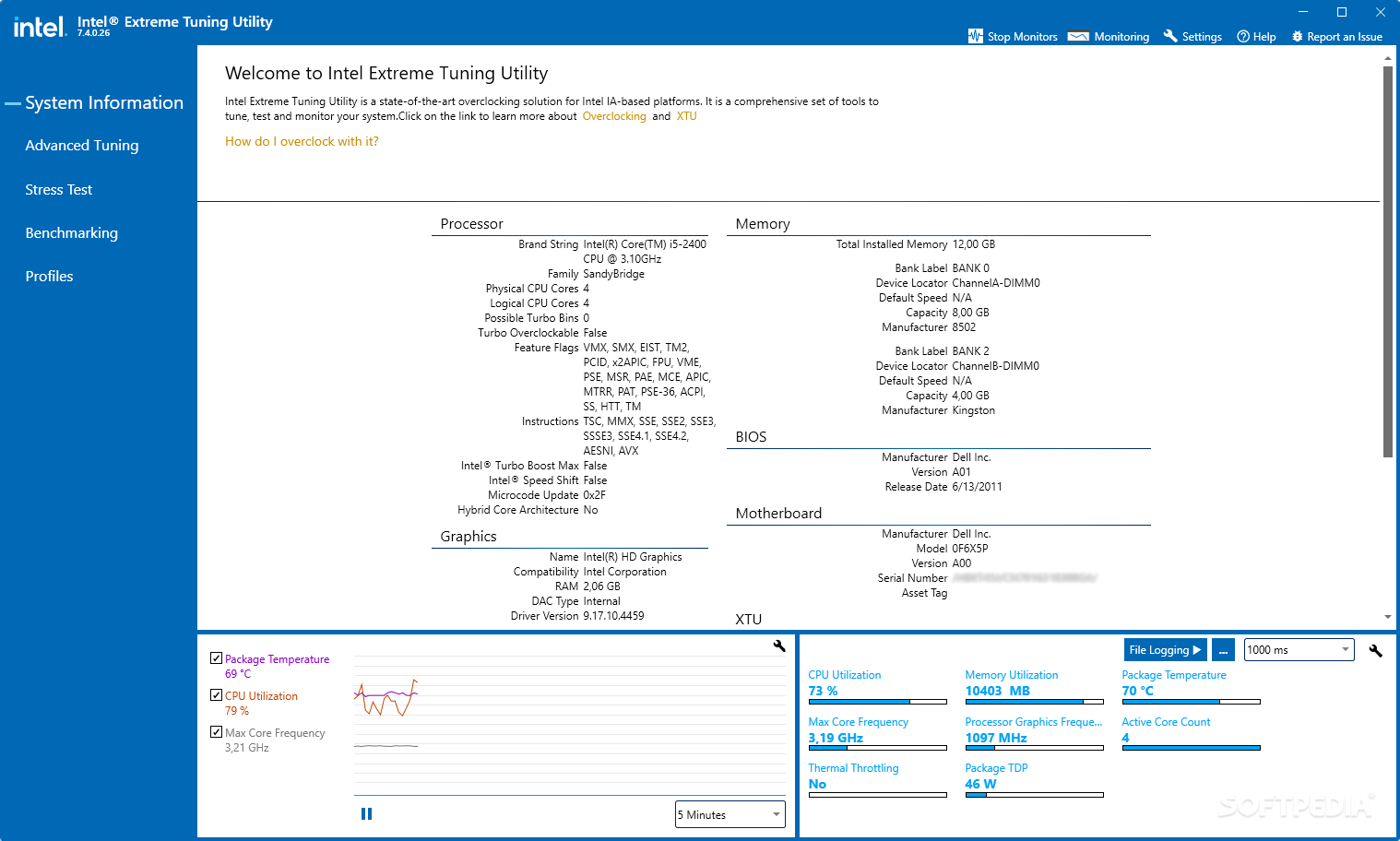
This number, in GHz, is the number you’re most likely to encounter when looking at basic CPU speed specifications. Simply put: BCLK x Multipliers = CPU Core Frequency.Įxample: 100 MHz (BCLK) x 44 (Core Multiplier) = 4400 MHz = 4.4 GHz. A higher core voltage also results in a higher heat output, and greater power consumption by the CPU. Higher voltage levels are required to obtain higher stable CPU frequencies, because faster speeds require more power. This is the main input voltage to the processor. These multipliers are applied to the base clock frequency, and the result is the core frequency, commonly measured in GHz. Multipliers or “core multipliers.” There is a single multiplier for each CPU core.This is the base frequency of your CPU, usually measured in GHz. The CPU frequency is determined by three factors: Because the processor’s frequency heavily impacts the effective computational speed of the CPU, the ultimate goal is to increase the frequency of the CPU in order to achieve faster performance. In order to overclock a processor, the overclocker intentionally increases the CPU operation frequency above the original stock specifications. Otherwise, we’re going to start with the basics and walk you through what you need to know to start overclocking your CPU.Īltering clock frequency or voltage may void any product warranties and reduce stability, security, performance, and life of the processor and other components.
OVERCLOCKING USING INTEL EXTREME TUNING UTILITY HOW TO
You can also learn how to use Intel® Performance Maximizer (Intel® PM) overclocking software to automatically complete this process for you if you have the latest Gen Intel® Core™ processor.
OVERCLOCKING USING INTEL EXTREME TUNING UTILITY MANUAL
If you’re looking for a more hands on, customizable approach, you can read about how to achieve a manual overclock using BIOS here. This all-in-one software does most of the heavy lifting for you, and allows for a streamlined overclocking process that is perfect for first timers.

The first, and easiest, involves using Intel® Extreme Tuning Utility (Intel® XTU). We’ve provided detailed instructions on two popular overclocking methods. We’re going to cover the basics of what overclocking is, how it works, and a few ways you can safely do it yourself. The process might seem complex, but the fundamentals of how to overclock are actually pretty straightforward. Overclocking your CPU is a great way to extract even more performance from your hardware.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
